Best Endocrinologist in Texas: Recognized Knowledge in Hormonal Medication
Wiki Article
The Science Behind Hormonal Agent Regulation: Insights From an Endocrinologist
The Scientific Research Behind Hormone Regulation: Insights From an Endocrinologist uses a detailed expedition of the elaborate procedures involved in hormone policy. Whether you are a medical specialist seeking a deeper understanding of endocrine function or a specific interested in learning regarding the scientific research behind hormone regulation, this publication is an indispensable source.Hormones and Their Features
Hormones play essential roles in the regulation and control of numerous physical processes within the body. These chemical messengers are produced by endocrine glands and are launched into the bloodstream, where they travel to target cells or body organs to apply their impacts. The functions of hormonal agents are diverse and incorporate nearly every aspect of human physiology.One of the main functions of hormones is to preserve homeostasis, which is the stable inner environment needed for the body to function ideally. Insulin, a hormonal agent generated by the pancreas, manages blood glucose degrees by advertising the uptake and storage of sugar in cells. Another hormonal agent, cortisol, aids the body react to stress by raising blood glucose levels and subduing the body immune system.
Hormones likewise play crucial roles in development and development. Development hormonal agent, created by the pituitary gland, promotes the growth of tissues and bones, while thyroid hormones regulate metabolic process and influence the growth of the nerves - Endocrinologist. In addition, reproductive hormonal agents, such as estrogen and testosterone, are accountable for the development and maintenance of additional sex-related qualities and the guideline of the menstruation
The Endocrine System: An Overview
Playing a crucial duty in the policy and coordination of physiological procedures, the endocrine system is a complicated network of glands that create and release hormones into the blood stream. These glands, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreatic, ovaries, and testes, produce hormones that act as chemical messengers, influencing different bodily features. The endocrine system functions in conjunction with the nerve system to keep and regulate homeostasis, making certain that the body's interior atmosphere remains steady.It creates hormonal agents that hinder the release or stimulate of hormonal agents from the pituitary gland, which in turn regulates the activity of other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland, situated in the neck, generates hormonal agents that manage metabolic rate and power equilibrium.
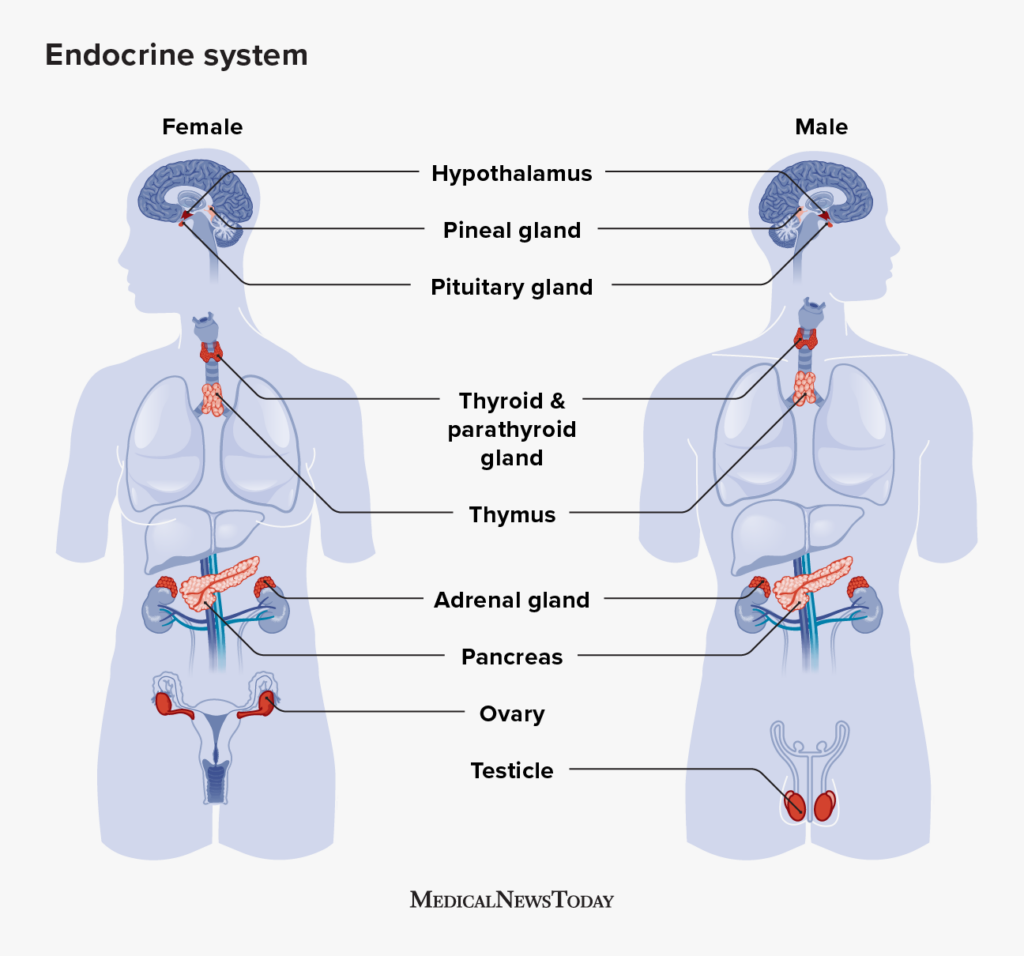
Policy of Hormonal Agent Manufacturing
The policy of hormonal agent manufacturing involves a complex interplay between various glands and feedback devices within the endocrine system. Hormonal agents are chemical messengers that play an important role in keeping homeostasis and working with different physical procedures in the body. The production of hormonal agents is snugly regulated to ensure the proper performance of the endocrine system.The hypothalamus, situated in the brain, serves as a key regulatory authority of hormone manufacturing. It launches hormones that hinder the manufacturing or boost of hormones by the pituitary gland, which is often referred to as the "master gland" of the endocrine system. The pituitary my blog gland, in turn, produces hormonal agents that act on various target glands throughout the body, promoting them to produce and release details hormones.
Feedback systems likewise play a crucial function in hormone law. When hormonal agent degrees climb above or drop listed below the optimal array, the body causes mechanisms to either decrease or rise hormonal agent manufacturing, specifically, to restore equilibrium.
Responses Loops in Hormonal Agent Law
Responses loops play a crucial function in the law of hormone manufacturing. These loopholes entail a collection of communications in between the endocrine glands, hormones, and target organs to maintain homeostasis in the body. There are two kinds of comments loops: unfavorable responses and positive responses.When hormonal agent degrees increase above a certain limit, the hypothalamus in the brain signals the pituitary gland to reduce hormonal agent production. Conversely, when hormonal agent levels drop below the threshold, the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland to raise hormonal agent production, bring back equilibrium.
Favorable responses loopholes, on the various other hand, amplify hormone manufacturing. This happens when a hormone boosts the launch of even more of the very same hormonal agent, bring about a fast boost in its degrees. However, favorable comments loopholes are much less common in hormone guideline and are usually associated with details physiological processes, such as giving birth and lactation.
Aspects Affecting Hormonal Agent Balance
Elements affecting hormonal agent balance include dietary options, way of living habits, and environmental direct exposures. These i thought about this variables can have a significant effect on the fragile balance of hormones in the body, impacting different physical procedures and total health.Dietary options play a crucial function in hormonal agent regulation. Consuming a balanced diet plan that consists of a selection of nutrients is important for preserving hormonal agent balance. Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, are especially important for optimal hormone function. On the other hand, a diet plan high in processed foods, improved sugars, and unhealthy fats can interrupt hormonal agent levels and result in imbalances.
Sufficient sleep is vital for hormonal agent production and regulation, as disrupted sleep patterns can lead to discrepancies. Additionally, chronic tension can dysregulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a crucial player in hormone policy, leading to a waterfall of hormone imbalances.

Final Thought
In conclusion, recognizing the scientific research behind hormone policy is crucial for maintaining overall health and wellness and wellness. Hormonal agents play important functions in different physical features, and their manufacturing is managed by intricate responses loopholes.The Scientific Research Behind Hormone Policy: Insights From an Endocrinologist offers a comprehensive expedition of the complex processes involved in hormonal agent guideline. It produces hormonal agents that boost or prevent the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, which in turn regulates the task of other endocrine glands. It releases hormonal agents that hinder the manufacturing or stimulate of hormonal agents by the pituitary gland, which is commonly referred to as the "master gland" of the endocrine system. The pituitary gland, in turn, creates hormones that act on numerous target glands throughout the body, promoting them to generate and release certain hormonal agents.
When hormone levels natural clinic climb above a specific limit, the hypothalamus in the brain signifies the pituitary gland to decrease hormone manufacturing. (Endocrinologist)
Report this wiki page